Understanding the food chain for deer reveals much about ecosystems. It highlights the balance between animals and their environment.
Deer are herbivores, meaning they eat plants. This simple fact places them as primary consumers in the food chain. They feed on a variety of vegetation, such as grasses, leaves, and fruits. This diet sustains them and impacts the plant life around them.
Predators like wolves and cougars rely on deer for survival, making deer a crucial part of the food web. By examining this chain, we see how each species plays a vital role. This balance is essential for maintaining healthy ecosystems. Exploring the food chain for deer gives us insight into nature’s intricate connections.
Introduction To Deer Diet
Deer are fascinating creatures known for their grace and elegance. Understanding their diet can help us appreciate their role in the ecosystem. The food chain of a deer includes various plants, shrubs, and occasionally, fruits. Let’s explore the natural feeding habits and the importance of diet for deer.
Natural Feeding Habits
Deer are primarily herbivores. They rely on a variety of plants for nutrition. Here is a breakdown of their natural feeding habits:
- Grasses: Deer often graze on tender grasses in open fields.
- Shrubs: They consume leaves and twigs from shrubs.
- Fruits: Deer enjoy fallen fruits, like apples and berries, when available.
- Nuts: Acorns and chestnuts are seasonal favorites.
| Food Type | Examples |
|---|---|
| Grasses | Bluegrass, Fescue |
| Shrubs | Sumac, Dogwood |
| Fruits | Apples, Berries |
| Nuts | Acorns, Chestnuts |
Importance Of Diet
A deer’s diet is crucial for its health and survival. Proper nutrition helps deer grow and reproduce. A balanced diet ensures strong antlers in males. Nutritious food supports energy levels, crucial for escaping predators.
In winter, food scarcity can affect deer populations. They rely on stored fat and available vegetation. Understanding their diet helps in wildlife conservation efforts.
- Nutrition: Supports growth and reproduction.
- Antlers: Strong diet leads to robust antlers.
- Energy: Essential for escaping predators.
Proper diet is essential for the overall well-being of deer. It impacts their health and ability to thrive in the wild.

Credit: www.youtube.com
Types Of Food Deer Consume
Deer are fascinating creatures with diverse diets. They consume various types of food depending on the season. Understanding what deer eat can help maintain a healthy ecosystem. Their diet consists of grasses, plants, fruits, and nuts.
Grasses And Plants
Deer love to graze on grasses. These provide essential nutrients. In the spring, they eat young shoots. During summer, they consume leafy plants. They seek out tender plants, which are easy to digest. Clover is a favorite among deer. They also eat a variety of wildflowers. These offer high nutritional value.
In winter, they shift to woody plants. They browse on twigs and bark. Evergreen plants also become a key food source. These provide much-needed sustenance during harsh conditions.
Fruits And Nuts
Fruits are a treat for deer. They enjoy apples, berries, and persimmons. These fruits are rich in sugars and vitamins. Deer consume them eagerly during the fall. It helps them store fat for winter.
Nuts are another important food source. Acorns are particularly favored. They are high in fats and proteins. Deer rely on them during autumn. They also eat other nuts like hickory and beech. This diet helps them prepare for the colder months.
Seasonal Variations In Diet
Deer adjust their diet with the seasons. In spring, they eat young plants and buds. In winter, they graze on woody plants and bark.
Deer’s diet changes with the seasons. Different food sources become available. Let’s explore how their diet shifts throughout the year.Spring And Summer
In spring, deer’s diet is rich and varied. New growth provides many options. Fresh grasses are abundant. Deer also eat tender leaves. Buds and shoots are plentiful. These foods are easy to digest. They offer high nutritional value. Deer also consume young plants. This helps them build strength. Summer brings more variety. Deer enjoy fruits and berries. They eat various herbs and flowers. Their diet includes mushrooms. They also consume more leafy greens. Summer foods keep deer healthy. They provide necessary vitamins and minerals.Fall And Winter
Fall brings changes to deer’s diet. Acorns and nuts become key. They provide energy for winter. Deer also eat fallen fruits. They consume more bark and twigs. These foods are harder to digest. But deer adapt to survive. Winter is the toughest season. Food is scarce and limited. Deer eat woody plants and shrubs. They consume evergreen leaves. Stored fat helps them survive. Deer also browse on available vegetation. Winter diet is less nutritious. But it sustains them through the cold months. “`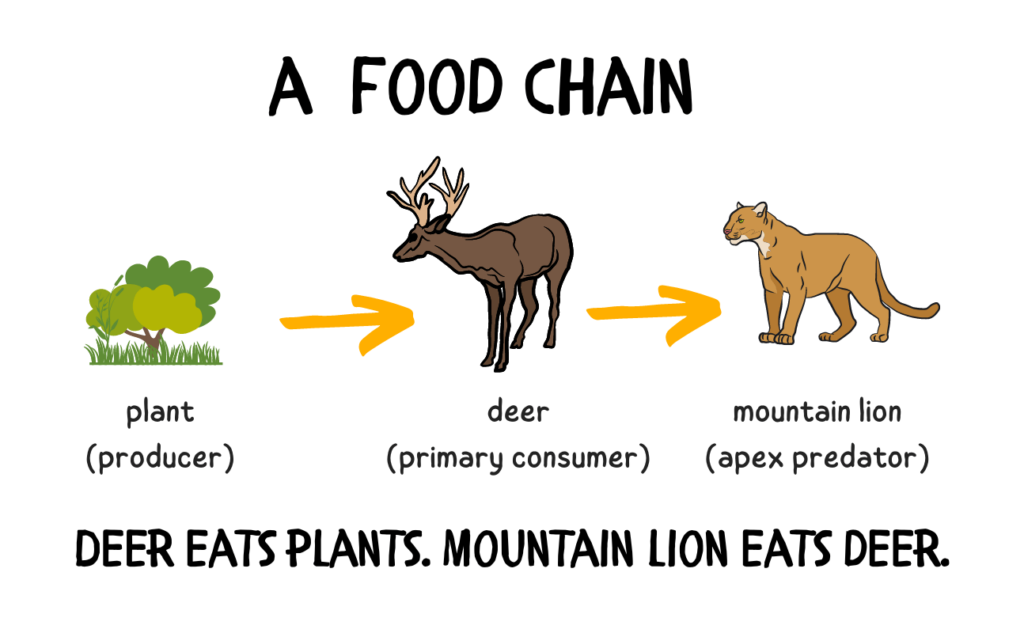
Credit: kids.mongabay.com
Nutritional Needs Of Deer
Deer have specific nutritional needs to stay healthy. Their diet must include a mix of essential nutrients. Deer graze on a variety of plants. These include grasses, leaves, and twigs. By doing so, they meet their nutritional requirements. Understanding these needs helps ensure deer thrive in their habitat.
Essential Nutrients
Deer require several essential nutrients. These include carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, and minerals. Carbohydrates provide energy. Proteins are vital for growth and repair. Fats help store energy. Vitamins and minerals support overall health. Each nutrient plays a crucial role. A balanced intake ensures optimal health and vitality.
Balancing The Diet
Balancing the diet of deer is key. They need a mix of different plants. This variety ensures they get all necessary nutrients. Seasonal changes affect their diet. In spring, they eat more green plants. In winter, they rely on twigs and bark. Understanding these patterns helps maintain their health. Proper diet balance supports their well-being.
Role Of Browsing In Deer Diet
The role of browsing in deer diet is crucial for their survival. Deer are herbivores, and browsing is a primary feeding activity. It helps them find various plants, leaves, and twigs to eat. This feeding behavior allows deer to meet their dietary needs effectively. Understanding what types of browse deer consume and their nutritional benefits can offer insights into their health and habitat requirements.
Types Of Browse
Deer browse includes a wide range of plant materials. They eat leaves, stems, buds, and bark from shrubs and trees. Some common browse plants are oak, willow, and birch. They also consume evergreen species like pine and fir. During different seasons, the types of browse available to deer may change. In winter, they may rely more on woody plants. During spring and summer, they have access to fresh leaves and herbaceous plants.
Nutritional Benefits
Browsing provides deer with essential nutrients. Leaves and stems offer vitamins and minerals. These nutrients support their growth and reproduction. Browsing also helps deer maintain a balanced diet. Woody plants provide fiber, which aids in digestion. Young, tender leaves are rich in protein, essential for muscle development. By consuming a variety of plants, deer ensure they get a mix of nutrients. This variety helps them stay healthy and strong throughout the year.
Impact Of Habitat On Diet
The impact of habitat on diet is crucial for understanding the food chain of deer. Different habitats provide varied food sources which affect the diet and health of deer. Let’s explore how forest habitats and grassland habitats influence what deer eat.
Forest Habitats
In forest habitats, deer have access to a rich variety of food. They feed on leaves, twigs, and bark from trees and shrubs. These areas also provide fruits and nuts that fall from trees. Below is a table showing common food sources for deer in forests:
| Food Source | Description |
|---|---|
| Leaves | From trees and shrubs |
| Twigs | Young, tender shoots |
| Bark | Outer covering of trees |
| Fruits | Apples, berries, and more |
| Nuts | Acorns, chestnuts |
Deer also eat fungi and lichens in forests. These items provide essential nutrients. Forests offer a balanced diet for deer. This helps in maintaining their health and energy.
Grassland Habitats
In grassland habitats, the diet of deer changes. They rely more on grasses and herbs. These areas are open and provide plenty of grazing opportunities. Below are the main food sources for deer in grasslands:
- Grasses: Different types of grass
- Herbs: Plants like clover and dandelions
- Forbs: Flowering plants
- Legumes: Peas and beans
Grasslands also provide seeds and grains. These are important for deer, especially in dry seasons. Deer adapt their diet based on availability. They may also eat young tree shoots found in grasslands.
Understanding the impact of habitat on diet helps in conserving deer populations. It ensures they have the right food sources to thrive in their environment.
Human Influence On Deer Diet
Human activities have a significant impact on the diet of deer. Changes in the environment due to agricultural practices and urban development alter their natural habitat. As a result, deer adapt their feeding habits to new food sources provided by human activities.
Agricultural Impact
Agriculture plays a major role in shaping the diet of deer. Farmers grow crops that attract deer, providing them with easy access to food. Deer often feed on:
- Corn
- Soybeans
These crops are highly nutritious, offering deer a rich diet. But this creates challenges for farmers, as deer feeding can damage crops. To mitigate this, some farmers use fences or repellents. This reduces the impact of deer on their fields.
Urbanization Effects
Urbanization leads to habitat fragmentation, forcing deer to adapt to urban settings. In cities, deer find food in:
- Gardens
- Parks
- Ornamental plants
Urban areas provide deer with a variety of plants not found in the wild. This includes shrubs, flowers, and even fruits. The presence of green spaces in cities offers deer continuous food supply. But this also leads to conflicts with residents who may find their gardens damaged.
Urban deer face other risks, such as traffic and human-wildlife interactions. Efforts to manage deer populations in cities include:
- Relocation programs
- Controlled hunting
- Public education on coexistence
These measures aim to balance the needs of urban wildlife and human communities.

Credit: www.shutterstock.com
Conservation And Deer Diet
Understanding the diet of deer is essential for their conservation. Deer play a significant role in the ecosystem. Their diet affects the health of forests and grasslands. Protecting their natural habitats and adopting sustainable feeding practices are crucial for their survival.
Protecting Natural Habitats
Natural habitats are vital for deer. They provide food, shelter, and breeding grounds. Forests, grasslands, and wetlands are essential habitats. Human activities, such as deforestation and urbanization, destroy these habitats. This leads to a loss of food sources for deer.
Conservation efforts aim to protect and restore these habitats. Planting native trees and preserving wetlands help maintain the balance. Wildlife corridors connect fragmented habitats. This allows deer to move freely and find food.
Sustainable Feeding Practices
Sustainable feeding practices ensure deer get the right nutrition. Feeding deer in the wild can be harmful. It disrupts their natural foraging behavior. It can also lead to overpopulation and disease spread.
Instead, support natural food sources. Planting native plants provides deer with their natural diet. Avoid feeding deer processed foods. They lack the nutrients deer need and can cause health problems.
Here are some sustainable practices:
- Plant native trees and shrubs
- Preserve natural water sources
- Avoid artificial feeding stations
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is The Primary Food Source For Deer?
Deer mainly eat plants, leaves, and grass. Their diet is herbivorous.
Where Do Deer Fit In The Food Chain?
Deer are primary consumers. They eat plants and are prey to predators.
What Animals Prey On Deer?
Wolves, lions, and bears hunt deer. They are natural predators.
How Do Deer Contribute To The Ecosystem?
Deer help in plant control. They spread seeds through their droppings.
Can Deer Adapt To Different Environments?
Yes, deer adapt well. They can live in forests, grasslands, and even urban areas.
Conclusion
A healthy food chain is crucial for deer survival. Deer rely on plants for nutrition. Predators help maintain a balanced ecosystem. We must protect habitats to ensure this balance. Understanding the food chain helps us appreciate nature’s complexity. Simple actions can support wildlife conservation.
Let’s work together to preserve deer and their environment. This effort benefits all creatures, including humans.